29+ What Is Unique About The Physical Geography Of Japan
Japan is an archipelago or string of islands on the eastern edge of Asia. The Japanese have worked at redesigning buildings to better withstand earthquakes.

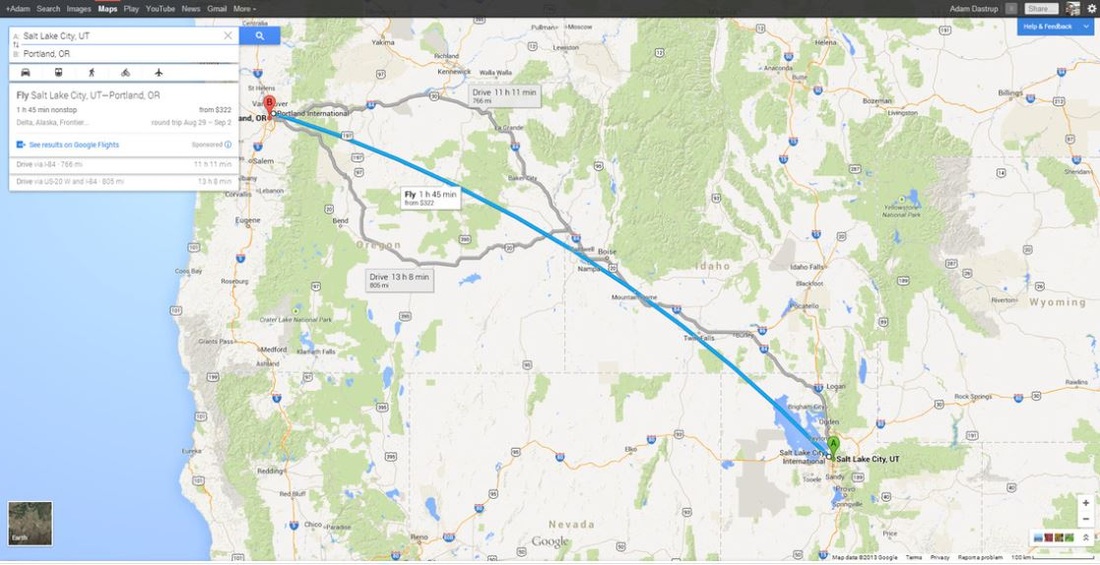
Physical Map Of Honshu Japan Map Sea Of Japan
Japan is an archipelago or string of islands on the eastern edge of Asia.

What is unique about the physical geography of japan. Volcanoes and earthquakes are common. Mount Fuji is the tallest mountain in Japan standing at 3776 meters 12380 feet. Not only is Japan an island country but it also is situated along the Ring of Fire a zone of frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions bordering the Pacific Ocean.
Japan is an island country with a very rugged landscape. These modest rivers and streams have necessitated hundreds of bridges in Tokyo including the central Nihonbashi from which all distances in Japan were traditionally measured. Start studying Physical geography of Japan and Koreas.
There are four main islands. There are also nearly 4000 smaller islands. Then due to a chain of many volcanic incidents it broke off forming todays Japan.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Mount Fuji is the tallest mountain in Japan. The Geography of Japan Around 400 million years ago Japan was a peninsula connected to the huge landmass known as Asia.
Japans geographic features are unique in several ways. Much of Japan is long narrow valleys between tree-covered low mountains either natural or reforested with strips of agriculture and human habitation along the valley edges. The islands have tall mountains originating from volcanic activity.
Japan is a mountainous country with relatively few areas of flat land. Japans nearest mainland neighbors are the Siberian region of Russia in the north and Korea and China farther south. The eastern half of the central city constituted the old commercial downtown district Shitamachi while the western hills Yamanote were home to metroplolitan Tokyos more affluent residential areas.
Many towns are famous for hot springs or onsen. Mountainous terrain covers about 80 percent of Japans land area leaving only about a small percentage of arable land or land suitable for farming. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
The physical area of all Japans islands is equivalent to about the size of the US state of Montana. Start studying Japan Geography. This physiography or physical.
At 3776 metres tall it poses a challenging climb for those that wish to climb it. There are four main islands Hokkaido Honshu Shikoku and Kyushu. There are also nearly 4000 smaller islands too.
The mountain contributes to Japans physical cultural and spiritual geography. Japan is located in the Pacific Ring of Fire and has 186 volcanoes of which about sixty are active. Hokkaido Honshu Shikoku and Kyushu.
Because of where it is located in the Pacific Japan has many different natural disasters. Japan has a multitude of islands surrounding it some of. Many of the volcanoes are active including the famous Mount Fuji.
The mountainous islands of Japan extend into two climate zones. The mountains in this image are exaggerated but they do give an excellent idea of how little flat land there is.